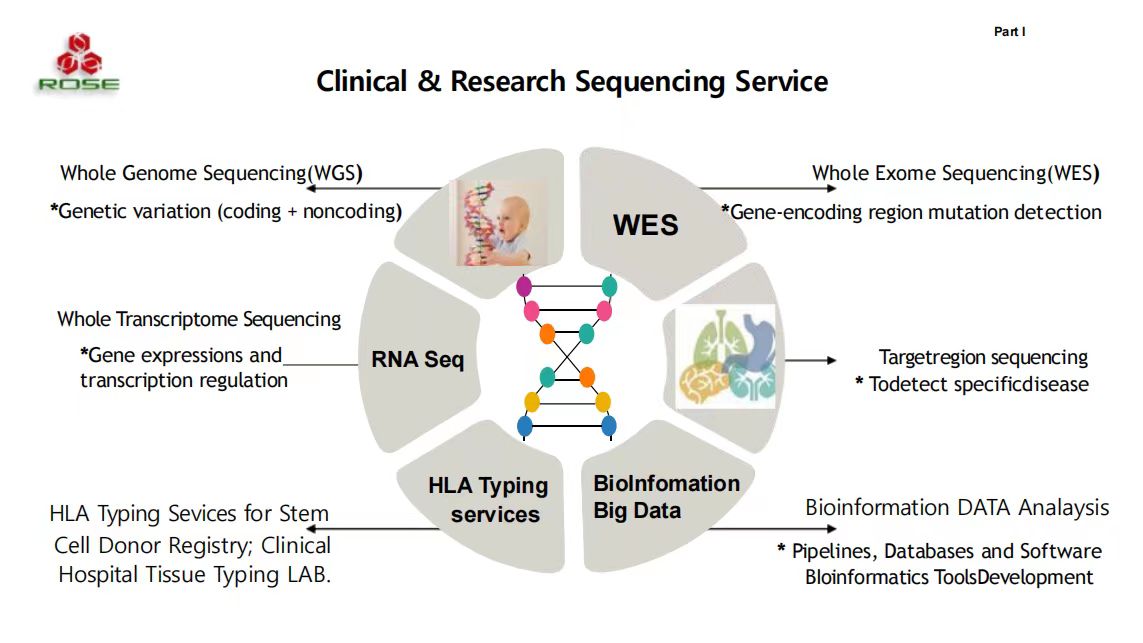
The purpose of genomics is to collectively characterize and quantify all genes of an organism, and to study their interrelationships and impacts on the organism. Genomics also includes genome sequencing and analysis, which assembles and analyzes the function and structure of the entire genome through the use of high-throughput DNA sequencing and bioinformatics. Genomics also studies phenomena within the genome, such as epistasis (the influence of one gene on another), pleiotropy (the influence of one gene on multiple traits), heterosis (hybridization activity), and interactions between motif site and alleles within the genome.