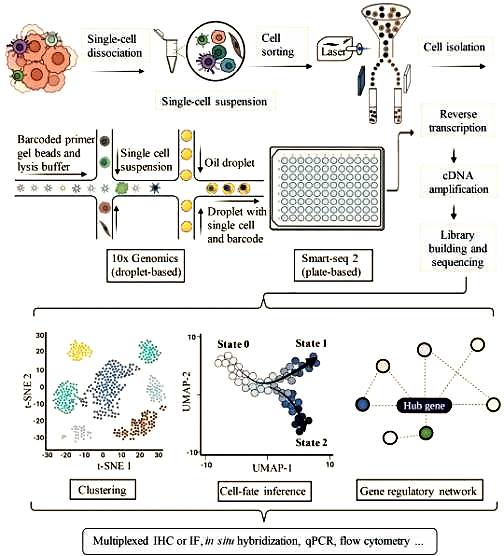
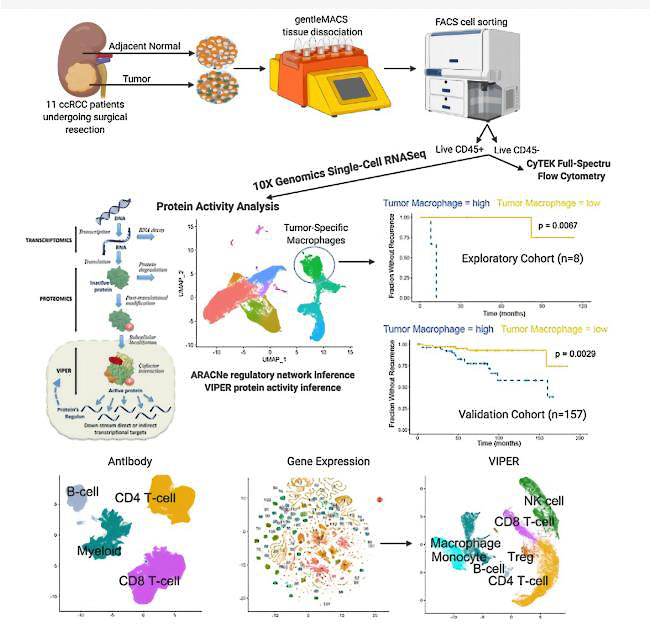
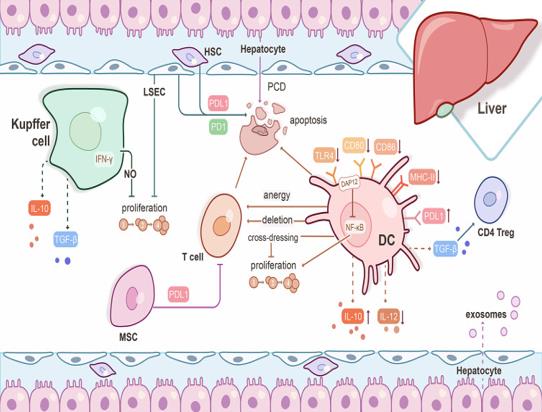
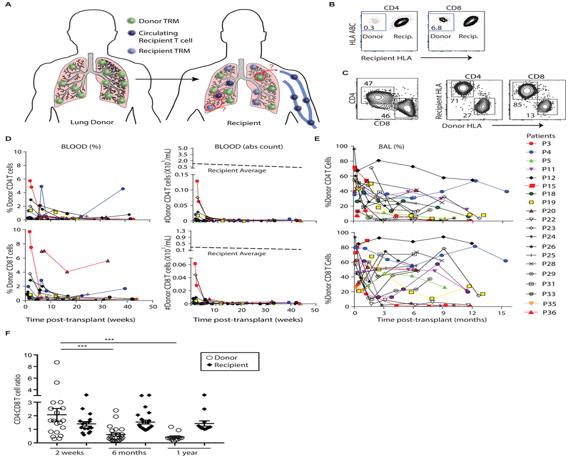
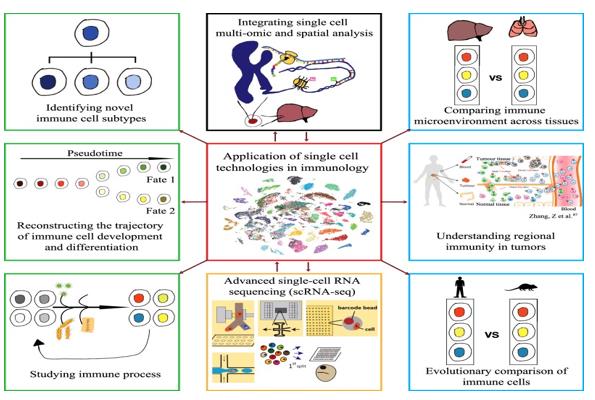
Application Of Single Cell Sequencing In Transplantation
At present, the main difficulties in successful transplantation include selecting the best matching donor and reducing lifelong immune suppression. For transplant rejection, the latest progress in scRNA seq provides an opportunity to fully reveal new cell types and states without result bias and RNA degradation A snapshot of the single-cell transcriptome shows different stages of immune differentiation and activation, which are rarely synchronized between cells. At single-cell resolution, it can describe immune cells, stromal cells, and new cell subtypes that suffer immune rejection, and further compare the unique characteristics of signaling pathways between different cell subpopulations. Here, we describe the effects of Scana-SEQ on the kidneys, liver, and liver, Advantages in the field of lung and hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) transplantation and immune applications.
T cells play a crucial role in transplant rejection. Most studies focus on bulk methods based on biopsy samples and do not provide information on t cell receptors (TCRs) αβ The lack of information on chain pairing may underestimate the actual differences in the library and cannot reflect that T cells with the same TCR can perform opposite biological functions. ScRNA seq technology overcomes the aforementioned limitations and makes library analysis more diverse.